Electron Configuration for Silver (Ag and Ag+ ion)
Silver is the 47th element in the periodic table and its symbol is ‘Ag’. Silver is a classified transition metal. In this article, I have discussed in detail how to easily write the complete electron configuration of silver.
What is the electron configuration of silver?
The total number of electrons in silver is forty-seven. These electrons are arranged according to specific rules in different orbitals.
The arrangement of electrons in silver in specific rules in different orbits and orbitals is called the electron configuration of silver.
The electron configuration of silver is [Kr] 4d10 5s1, if the electron arrangement is through orbitals. Electron configuration can be done in two ways.
- Electron configuration through orbit (Bohr principle)
- Electron configuration through orbital (Aufbau principle)
Electron configuration through orbitals follows different principles. For example Aufbau principle, Hund’s principle, and Pauli’s exclusion principle.
Electron configuration of silver through orbit
Scientist Niels Bohr was the first to give an idea of the atom’s orbit. He provided a model of the atom in 1913. The complete idea of the orbit is given there.
The electrons of the atom revolve around the nucleus in a certain circular path. These circular paths are called orbit(shell). These orbits are expressed by n. [n = 1,2,3,4 . . . The serial number of the orbit]
K is the name of the first orbit, L is the second, M is the third, and N is the name of the fourth orbit. The electron holding capacity of each orbit is 2n2.
| Shell Number (n) | Shell Name | Electrons Holding Capacity (2n2) |
| 1 | K | 2 |
| 2 | L | 8 |
| 3 | M | 18 |
| 4 | N | 32 |
For example,
- n = 1 for K orbit.
The maximum electron holding capacity in K orbit is 2n2 = 2 × 12 = 2. - For L orbit, n = 2.
The maximum electron holding capacity in L orbit is 2n2 = 2 × 22 = 8. - n=3 for M orbit.
The maximum electron holding capacity in M orbit is 2n2 = 2 × 32 = 18. - n=4 for N orbit.
The maximum electron holding capacity in N orbit is 2n2 = 2 × 42 = 32.
Therefore, the maximum electron holding capacity in the first shell is two, the second shell is eight and the 3rd shell can have a maximum of eighteen electrons. The atomic number is the number of electrons in that element.
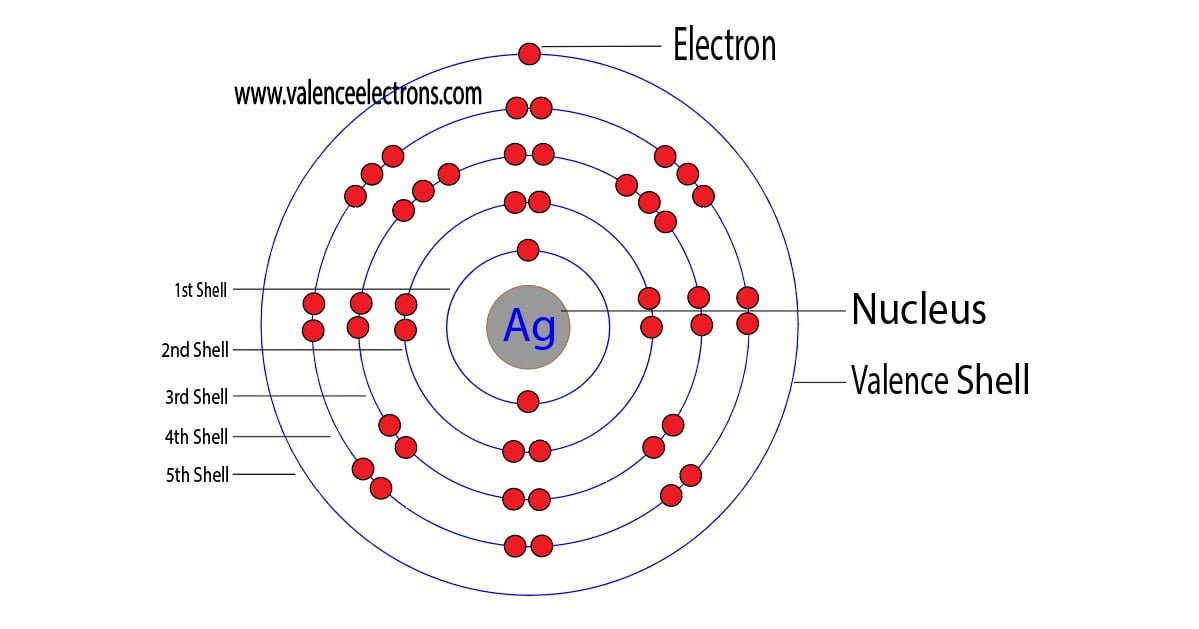
The atomic number of silver is 47. That is, the number of electrons in silver is forty-seven. Therefore, a silver atom will have two electrons in the first shell, eight in the 2nd orbit, and eighteen electrons in the 3rd shell.
According to Bohr’s formula, the fourth shell will have nineteen electrons but the fourth shell of silver will have eighteen electrons and the remaining one electron will be in the fifth shell.
Therefore, the order of the number of electrons in each shell of the silver atom is 2, 8, 18, 18, 1. Electrons can be arranged correctly through orbits from elements 1 to 18.
The electron configuration of an element with an atomic number greater than 18 cannot be properly determined according to the Bohr atomic model. The electron configuration of all the elements can be done through the orbital diagram.
Electron configuration of silver through orbital
Atomic energy shells are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are also called orbital. The most probable region of electron rotation around the nucleus is called the orbital.
The sub-energy levels depend on the azimuthal quantum number. It is expressed by ‘l’. The value of ‘l’ is from 0 to (n – 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, and f.
| Orbit Number | Value of ‘l’ | Number of subshells | Number of orbital | Subshell name | Electrons holding capacity | Electron configuration |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1s | 2 | 1s2 |
| 2 | 0 1 | 2 | 1 3 | 2s 2p | 2 6 | 2s2 2p6 |
| 3 | 0 1 2 | 3 | 1 3 5 | 3s 3p 3d | 2 6 10 | 3s2 3p6 3d10 |
| 4 | 0 1 2 3 | 4 | 1 3 5 7 | 4s 4p 4d 4f | 2 6 10 14 | 4s2 4p6 4d10 4f14 |
For example,
- If n = 1,
(n – 1) = (1–1) = 0
Therefore, the value of ‘l’ is 0. So, the sub-energy level is 1s. - If n = 2,
(n – 1) = (2–1) = 1.
Therefore, the value of ‘l’ is 0, 1. So, the sub-energy levels are 2s, and 2p. - If n = 3,
(n – 1) = (3–1) = 2.
Therefore, the value of ‘l’ is 0, 1, 2. So, the sub-energy levels are 3s, 3p, and 3d. - If n = 4,
(n – 1) = (4–1) = 3
Therefore, the value of ‘l’ is 0, 1, 2, 3. So, the sub-energy levels are 4s, 4p, 4d, and 4f. - If n = 5,
(n – 1) = (n – 5) = 4.
Therefore, l = 0,1,2,3,4. The number of sub-shells will be 5 but 4s, 4p, 4d, and 4f in these four subshells it is possible to arrange the electrons of all the elements of the periodic table.
| Subshell name | Name source | Value of ‘l’ | Value of ‘m’ (0 to ± l) | Number of orbital (2l+1) | Electrons holding capacity 2(2l+1) |
| s | Sharp | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| p | Principal | 1 | −1, 0, +1 | 3 | 6 |
| d | Diffuse | 2 | −2, −1, 0, +1, +2 | 5 | 10 |
| f | Fundamental | 3 | −3, −2, −1, 0, +1, +2, +3 | 7 | 14 |
The orbital number of the s-subshell is one, three in the p-subshell, five in the d-subshell and seven in the f-subshell. Each orbital can have a maximum of two electrons.
The sub-energy level ‘s’ can hold a maximum of two electrons, ‘p’ can hold a maximum of six electrons, ‘d’ can hold a maximum of ten electrons, and ‘f’ can hold a maximum of fourteen electrons.

Aufbau is a German word, which means building up. The main proponents of this principle are scientists Niels Bohr and Pauli. The Aufbau method is to do electron configuration through the sub-energy level.
The Aufbau principle is that the electrons present in the atom will first complete the lowest energy orbital and then gradually continue to complete the higher energy orbital.
The energy of an orbital is calculated from the value of the principal quantum number ‘n’ and the azimuthal quantum number ‘l’. The orbital for which the value of (n + l) is lower is the low energy orbital and the electron will enter that orbital first.
| Orbital | Orbit (n) | Azimuthal quantum number (l) | Orbital energy (n + l) |
| 3d | 3 | 2 | 5 |
| 4s | 4 | 0 | 4 |
Here, the energy of 4s orbital is less than that of 3d. So, the electron will enter the 4s orbital first and enter the 3d orbital when the 4s orbital is full. The method of entering electrons into orbitals through the Aufbau principle is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p 6s 4f 5d 6p 7s 5f 6d.
The first two electrons of silver enter the 1s orbital. The s-orbital can have a maximum of two electrons. Therefore, the next two electrons enter the 2s orbital.
The p-orbital can have a maximum of six electrons. So, the next six electrons enter the 2p orbital. The second orbit is now full. So, the remaining electrons will enter the third orbit.
Then two electrons will enter the 3s orbital and the next six electrons will be in the 3p orbital of the third orbit. The 3p orbital is now full. So, the next two electrons will enter the 4s orbital and ten electrons will enter the 3d orbital.
The 3d orbital is now full. So, the next six electrons enter the 4p orbital. The 4p orbital is now full. So, the next two electrons will enter the 5s orbital and the remaining nine electrons will enter the 4d orbital.
But the orbital wants to be half-filled or full-filled by electrons. Because the atom may be in a more stable state when the orbital is half-filled and full-filled.
Therefore, an electron of the 5s orbital completes a full-filled 4d orbital by jumping into the 4d orbital. Therefore, the silver complete electron configuration will be 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s1.
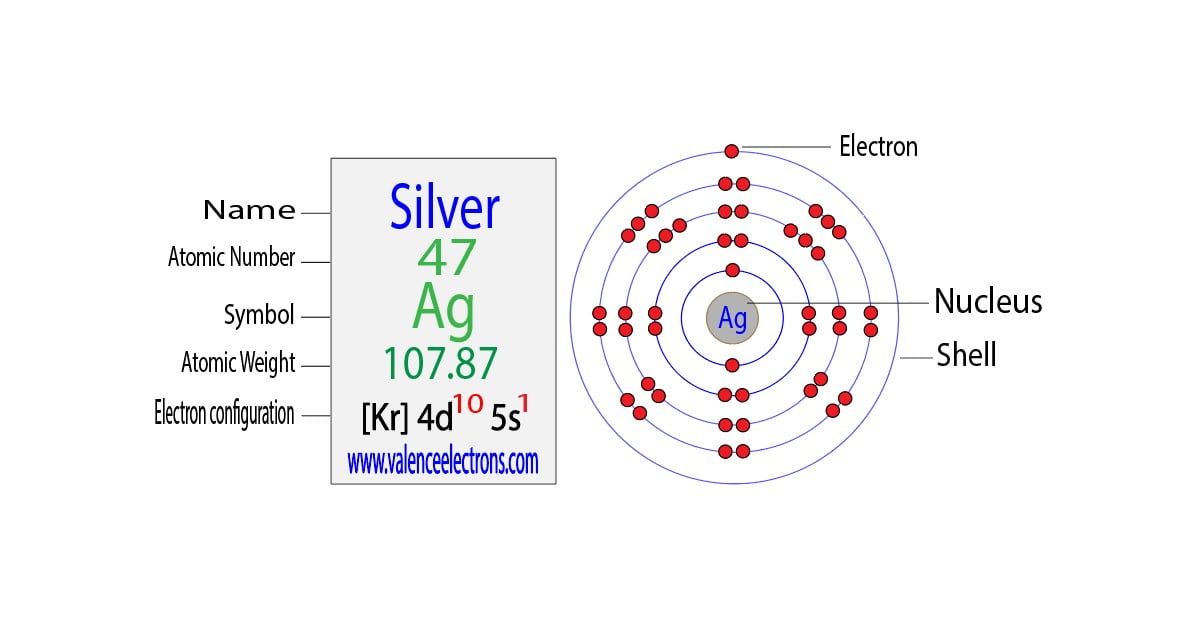
Note: The abbreviated electron configuration of silver is [Kr] 4d10 5s1. When writing an electron configuration, you have to write serially.
Silver ion(Ag+) electron configuration
The ground-state electron configuration of silver is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s1. This electron configuration shows that the last shell of silver has an electron and the d-orbital has a total of ten electrons. Therefore, the valence electrons of silver are one.
The elements that form bonds by donating electrons are called cation. The silver atom donates an electron in the 5s orbital to convert a silver ion(Ag+).
Ag – e– → Ag+
The electron configuration of silver ion(Ag+) is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10.
This electron configuration shows that the silver ion(Ag+) has four shells and the last shell has eighteen electrons and it achieves a stable electron configuration. Silver atoms exhibit +1 oxidation state.
FAQs
What is the symbol for silver?
Ans: The symbol for silver is ‘Ag’.
How many electrons does silver have?
Ans: 47 electrons.
How do you write the full electron configuration for silver?
Ans: Full electron configuration for silver is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s1.
How many valence electrons does silver have?
Ans: One valence electrons. The last shell of silver has an electron and the d-orbital has a total of ten electrons. Therefore, the valence electrons of silver are one.
What is the valency of silver?
Ans: The valency of silver is 1.
What is the abbreviated electron configuration for silver?
Ans: The abbreviated electron configuration for silver [Kr] 4d10 5s1.
How many electron shells does silver have?
Ans: Silver has a total of five electron shells.
What is the electron configuration of silver in the ground state?
Ans: The electron configuration of silver in the ground state is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 5s1.
How many orbitals does silver have?
Ans: 24 orbitals. The orbital number of the s-subshell is one, three in the p-subshell, five in the d-subshell, and seven in the f-subshell. Each orbital can have a maximum of two electrons.
How many electrons does silver have in its outer shell?
Ans: One electron. Silver atoms will have two electrons in the first shell, eight in the 2nd orbit, and eighteen electrons in the 3rd shell. According to Bohr’s formula, the fourth shell will have nineteen electrons but the fourth shell of silver will have eighteen electrons and the remaining one electron will be in the fifth shell.
How many electrons do you need to put in the 4d to get to silver (Ag)?
Ans: Ten electrons. The orbital wants to be half-filled or full-filled by electrons. Because the atom may be in a more stable state when the orbital is half-filled and full-filled. Therefore, an electron of the 5s orbital completes a full-filled 4d orbital by jumping into the 4d orbital.
How many electrons are in the 5s sublevel in the ground state configuration of silver?
Ans: One electron.
How many unpaired electrons does silver have?
Ans: One electron. Because the electron configuration for silver is [Kr] 4d10 5s1. Here, the 4d orbital is full of ten electrons. Only 5s orbital has one unpaired electron.
What is the highest energy-occupied sublevel for silver?
Ans: 4d. Because the energy of an orbital is calculated from the value of the principal quantum number ‘n’ and the azimuthal quantum number ‘l’. The formula for determining orbital energy is (n + l). Here, the energy of 4d orbital is 6 (4+2).
How many energy levels does silver have?
Ans: Silver has a total of five energy levels.
What is the last sublevel in silver?
Ans: 4d. Because 4d is the highest-energy occupied sublevel for silver.