Complete Electron Configuration for Argon (Ar)
Argon is the 18th element in the periodic table and its symbol is ‘Ar’. In this article, I have discussed in detail how to easily write the complete electron configuration of argon.
What is the electron configuration of argon?
The total number of electrons in argon is eighteen. These electrons are arranged according to specific rules in different orbitals.
The arrangement of electrons in argon in specific rules in different orbits and orbitals is called the electron configuration of argon.
The electron configuration of argon is [Ne] 3s2 3p6, if the electron arrangement is through orbitals. Electron configuration can be done in two ways.
- Electron configuration through orbit (Bohr principle)
- Electron configuration through orbital (Aufbau principle)
Electron configuration through orbitals follows different principles. For example Aufbau principle, Hund’s principle, and Pauli’s exclusion principle.
Electron configuration of argon through orbit
Scientist Niels Bohr was the first to give an idea of the atom’s orbit. He provided a model of the atom in 1913. The complete idea of the orbit is given there.
The electrons of the atom revolve around the nucleus in a certain circular path. These circular paths are called orbit(shell). These orbits are expressed by n. [n = 1,2,3,4 . . . The serial number of the orbit]
K is the name of the first orbit, L is the second, M is the third, and N is the name of the fourth orbit. The electron holding capacity of each orbit is 2n2.
| Shell Number (n) | Shell Name | Electrons Holding Capacity (2n2) |
| 1 | K | 2 |
| 2 | L | 8 |
| 3 | M | 18 |
| 4 | N | 32 |
For example,
- n = 1 for K orbit.
The maximum electron holding capacity in K orbit is 2n2 = 2 × 12 = 2. - For L orbit, n = 2.
The maximum electron holding capacity in L orbit is 2n2 = 2 × 22 = 8. - n=3 for M orbit.
The maximum electrons holding capacity in M orbit is 2n2 = 2 × 32 = 18. - n=4 for N orbit.
The maximum electrons holding capacity in N orbit is 2n2 = 2 × 42 = 32.
Therefore, the maximum electron holding capacity in the first shell is two, the second shell is eight and the 3rd shell can have a maximum of eighteen electrons. The atomic number is the number of electrons in that element.
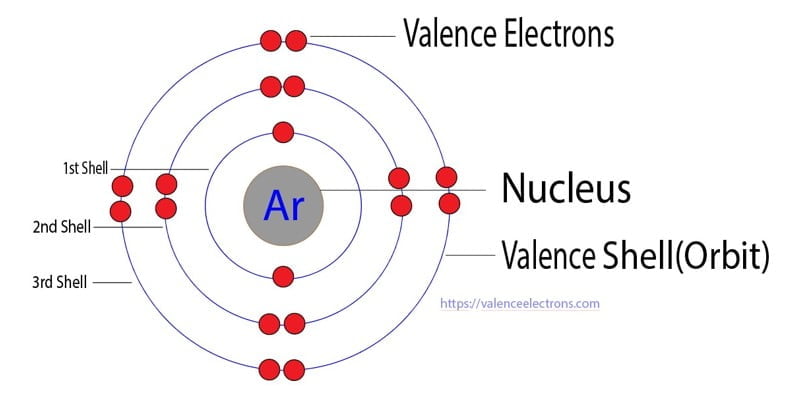
The atomic number of argon is 18. That is, the number of electrons in argon is eighteen. Therefore, the argon atom will have two electrons in the first shell, eight in the 2nd orbit, and eight electrons in the 3rd shell.
Therefore, the order of the number of electrons in each shell of the argon(Ar) atom is 2, 8, 8. Electrons can be arranged correctly through orbits from elements 1 to 18.
The electron configuration of an element with an atomic number greater than 18 cannot be properly determined according to the Bohr atomic model. The electron configuration of all the elements can be done through orbital diagrams.
Electron configuration of argon through orbital
Atomic energy shells are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are also called orbital. The most probable region of electron rotation around the nucleus is called the orbital.
The sub-energy levels depend on the azimuthal quantum number. It is expressed by ‘l’. The value of ‘l’ is from 0 to (n – 1). The sub-energy levels are known as s, p, d, and f.
| Orbit Number | Value of ‘l’ | Number of subshells | Number of orbital | Subshell name | Electrons holding capacity | Electron configuration |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1s | 2 | 1s2 |
| 2 | 0 1 | 2 | 1 3 | 2s 2p | 2 6 | 2s2 2p6 |
| 3 | 0 1 2 | 3 | 1 3 5 | 3s 3p 3d | 2 6 10 | 3s2 3p6 3d10 |
| 4 | 0 1 2 3 | 4 | 1 3 5 7 | 4s 4p 4d 4f | 2 6 10 14 | 4s2 4p6 4d10 4f14 |
For example,
- If n = 1,
(n – 1) = (1–1) = 0
Therefore, the value of ‘l’ is 0. So, the sub-energy level is 1s. - If n = 2,
(n – 1) = (2–1) = 1.
Therefore, the value of ‘l’ is 0, 1. So, the sub-energy levels are 2s, and 2p. - If n = 3,
(n – 1) = (3–1) = 2.
Therefore, the value of ‘l’ is 0, 1, 2. So, the sub-energy levels are 3s, 3p, and 3d. - If n = 4,
(n – 1) = (4–1) = 3
Therefore, the value of ‘l’ is 0, 1, 2, 3. So, the sub-energy levels are 4s, 4p, 4d, and 4f. - If n = 5,
(n – 1) = (n – 5) = 4.
Therefore, l = 0,1,2,3,4. The number of sub-shells will be 5 but 4s, 4p, 4d, and 4f in these four subshells it is possible to arrange the electrons of all the elements of the periodic table.
| Sub-shell name | Name source | Value of ‘l’ | Value of ‘m’ (0 to ± l) | Number of orbital (2l+1) | Electrons holding capacity 2(2l+1) |
| s | Sharp | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| p | Principal | 1 | −1, 0, +1 | 3 | 6 |
| d | Diffuse | 2 | −2, −1, 0, +1, +2 | 5 | 10 |
| f | Fundamental | 3 | −3, −2, −1, 0, +1, +2, +3 | 7 | 14 |
The orbital number of the s-subshell is one, three in the p-subshell, five in the d-subshell and seven in the f-subshell. Each orbital can have a maximum of two electrons.
The sub-energy level ‘s’ can hold a maximum of two electrons, ‘p’ can hold a maximum of six electrons, ‘d’ can hold a maximum of ten electrons, and ‘f’ can hold a maximum of fourteen electrons.

Aufbau is a German word, which means building up. The main proponents of this principle are scientists Niels Bohr and Pauli. The Aufbau method is to do electron configuration through the sub-energy level.
The Aufbau principle is that the electrons present in the atom will first complete the lowest energy orbital and then gradually continue to complete the higher energy orbital.
The energy of an orbital is calculated from the value of the principal quantum number ‘n’ and the azimuthal quantum number ‘l’. The orbital for which the value of (n + l) is lower is the low energy orbital and the electron will enter that orbital first.
| Orbital | Orbit (n) | Azimuthal quantum number (l) | Orbital energy (n + l) |
| 3d | 3 | 2 | 5 |
| 4s | 4 | 0 | 4 |
Here, the energy of 4s orbital is less than that of 3d. So, the electron will enter the 4s orbital first and enter the 3d orbital when the 4s orbital is full.
The method of entering electrons into orbitals through the Aufbau principle is 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p 5s 4d 5p 6s 4f 5d 6p 7s 5f 6d.
The first two electrons of argon enter the 1s orbital. The s-orbital can have a maximum of two electrons. Therefore, the next two electrons enter the 2s orbital.
The p-orbital can have a maximum of six electrons. So, the next six electrons enter the 2p orbital. The second orbit is now full. So, the remaining electrons will enter the third orbit.
Then two electrons will enter the 3s orbital of the third orbit and the remaining six electrons will be in the 3p orbital. Therefore, the argon complete electron configuration will be 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6.
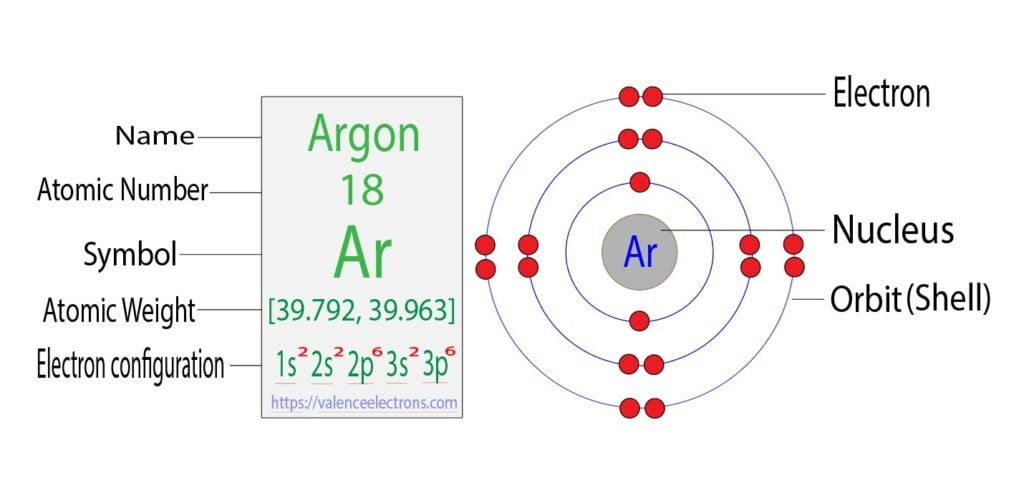
Note: The unabbreviated electron configuration of argon is [Ne] 3s2 3p6. When writing an electron configuration, you have to write serially.
Video for Argon Electron Configuration
What is the valency of argon?
After arranging the electrons, we have seen that the last shell of the argon atom has eight electrons. Therefore, the valence electrons of argon are eight. The ability of an atom of an element to join another atom during the formation of a molecule is called valency(valence).
The number of unpaired electrons in the last orbit of an element is the valency of that element. The electron configuration of argon shows that the argon atom has no unpaired electrons. Therefore, the valency of the argon atom is 0.
Why is argon an inert gas?
The elements in group-18 of the periodic table are inert gases. The inert gases of Group-18 are helium(He), neon(Ne), argon(Ar), krypton(Kr), xenon(Xe), and radon(Rn). We know that the element in group-18 is argon.
The electron configuration of argon shows that the orbit at the end of argon is filled with electrons. Argon does not want to exchange or share any electrons because the last orbit of argon is full of electrons.
And argon does not form any compounds because it does not share any electrons. They do not participate in chemical bonding and chemical reactions. For this, they are called inert elements.
The inert elements are in the form of gases at normal temperatures. For this inert elements are called inert gases. Again for this same reason, inert gas is called a noble gas.
FAQs
What is the symbol for argon?
The symbol for argon is ‘Ar’.
How many electrons does argon have?
18 electrons.
How do you write the full electron configuration for argon?
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6.
How many valence electrons does argon have?
Eight valence electrons.
What is the valency of argon?
The valency of argon is 0.