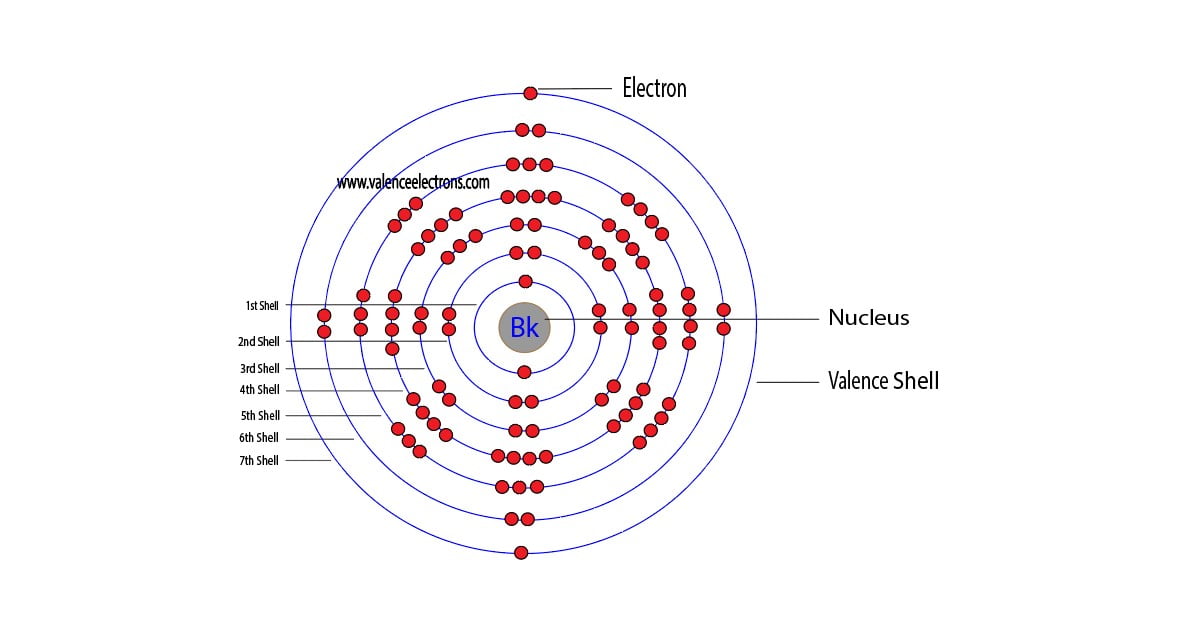
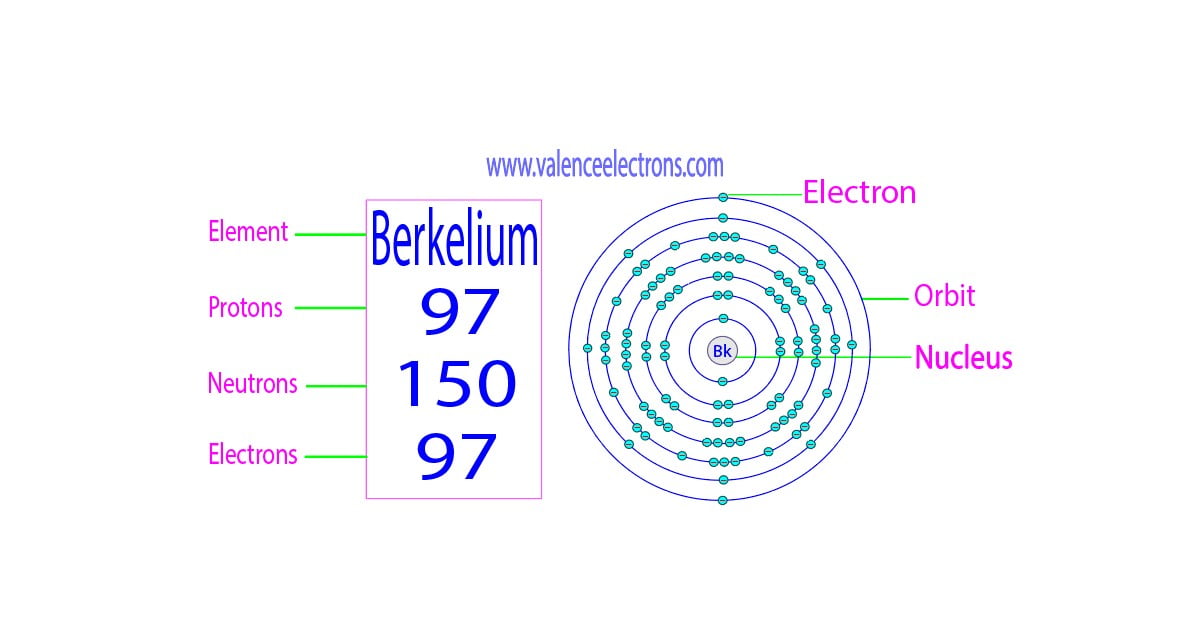
Protons, Neutrons, Electrons for Berkelium (Bk, Bk3+)
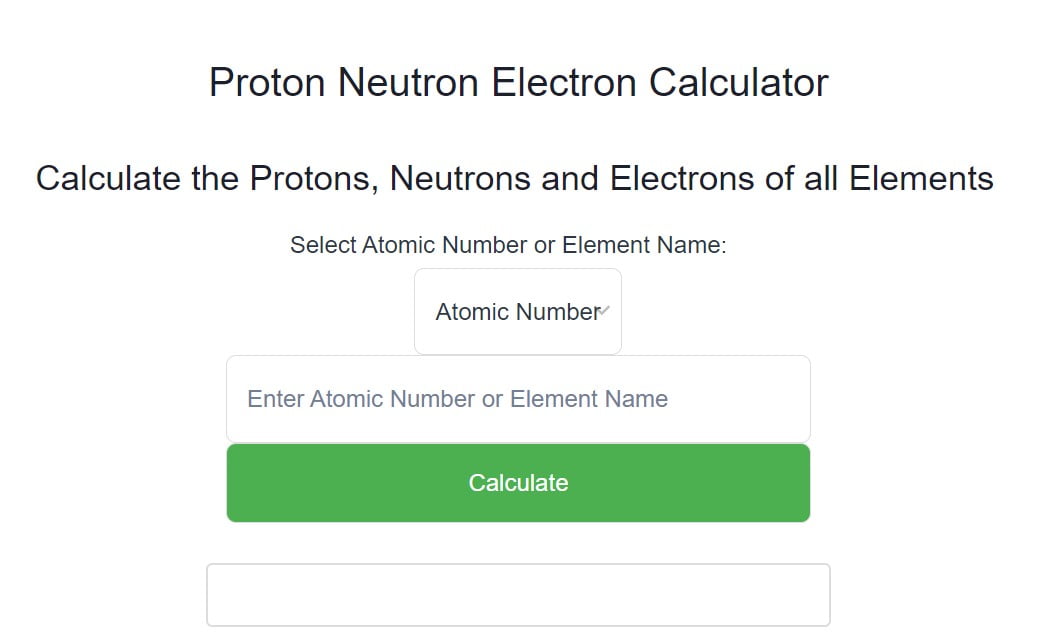
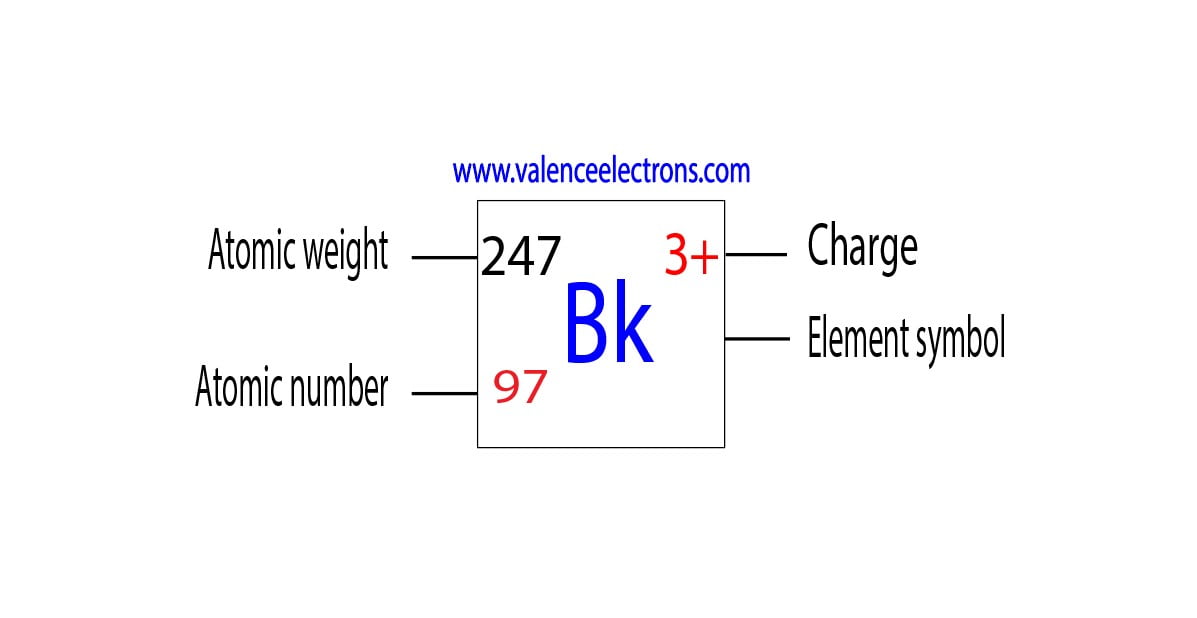
Berkelium is a classified actinide element and its symbol is ‘Bk’. Berkelium is the 97th element of the periodic table so its atomic number is 97.
The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons and electrons in that element. Therefore, a berkelium atom has ninety-seven protons and ninety-seven electrons.
The number of neutrons in an atom can be determined by the difference between the atomic mass and the number of protons.
The difference between the mass number of the berkelium atom and the number of protons is one hundred fifty. Therefore, a berkelium atom has one hundred fifty neutrons.
The number of neutrons depends on the isotope of the element. The berkelium atom has no stable isotope.
This article discussed in detail how to easily find the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in a berkelium atom.
Also discussed are the position of electrons, protons, and neutrons in an atom, the number of atomic masses, and the isotopes of berkelium. Hopefully, after reading this article you will know the details about this topic.
Where are the electrons, protons and neutrons located in an atom?
An atom is the smallest particle of an element that has no independent existence but is directly involved in chemical reactions as the smallest unit. Atoms are so small particles that they cannot be seen even under a powerful microscope.
The diameter of an atom of hydrogen is 0.1nm (1.0nm = 10-9m). So, if 1000 crore atoms of hydrogen are arranged side by side, it will be 1 meter long.
However, it has been possible to detect atoms by increasing the vision of a very powerful electron microscope by two million times. Numerous permanent and temporary particles exist in the atom.
Electrons, protons, and neutrons are located in the atom as permanent particles. Also, neutrino, antineutrino, positron, and mason are located in an atom as temporary particles.

Atoms can usually be divided into two parts. One is the nucleus and the other is the orbit. Experiments by various scientists have shown that the nucleus of an atom contains protons and neutrons.
The only exception is hydrogen, which has only protons in its nucleus but no neutrons. Electrons revolve around the nucleus in a specific orbit.
How to easily find the number of electrons, protons and neutrons in a berkelium atom?
Scientist Henry Gwynn Jefferies Mosle examined the X-ray spectrum of various elements from 1913 to 1914. The results of his experiments show that each element has a unique integer equal to the number of positive charges in the nucleus of that element.
He called that number the order of the atoms. Thus, the number of positive charges present in the nucleus of an element is called the atomic number of that element. The atomic number of the element is expressed by ‘Z’.
This number is equal to the serial number of the periodic table. We know that protons are located in the nucleus of an atom as a positive charge.
That is, the atomic number is the total number of protons. The atom is overall charge neutral. Therefore, the number of negatively charged electrons orbiting in its orbit is equal to the number of positively charged protons in the nucleus.
Atomic number (Z) = Number of charges in the nucleus (p)
How many protons does a berkelium atom have?
Protons are the permanent core particles of an atom. It resides in the center or nucleus of the atom. When a hydrogen atom removes an electron from its orbit, the positively charged particle that remains is called a proton. Hence, the proton is expressed by H+.
The relative mass of protons is 1, which is approximately equal to the mass of hydrogen (1.00757 amu). However, the actual mass of the proton is 1.6726 × 10−27 kg. That is, the mass of a proton is approximately 1837 times greater than the mass of an electron.
Proton is a positively charged particle. Its actual charge is +1.602 × 10−19 coulombs. The diameter of a proton particle is about 2.4 × 10−13 cm.
There are 118 elements in the periodic table and the 97th of these elements is berkelium. The elements in the periodic table are arranged according to their atomic number. Since berkelium is the 97th element of the periodic table, the atomic number of berkelium is 97.
We must always remember that the atomic number and the number of protons of an element are equal. Therefore, a berkelium atom contains ninety-seven protons.
How many electrons does a berkelium atom have?
Electrons are the permanent core particles of an atom. It resides in a specific orbit of the atom and revolves around the nucleus. The properties of the elements and their compounds depend on the electron configuration.
In 1897, scientist J. J. Thomson discovered the existence of electrons through cathode ray examination. The smallest of the permanent core particles of an atom is the electron. Its mass is about 1/1836 of the mass of a hydrogen atom.
The actual mass of the electron is 9.1085 × 10−28 g or 9.1093 × 10−31 kg. The mass of the electron is often ignored because this mass is too small. Electrons always provide a negative charge.
It is expressed by e–. The charge of electrons is –1.609 × 10–19 coulombs and the relative charge is –1. That is, the charge of an electron is equal to that of a proton but the opposite.
We must also remember that the number of protons and electrons in an element is equal. Therefore, a berkelium atom contains ninety-seven electrons in its orbits.
How many neutrons does a berkelium atom have?
Scientist Chadwick discovered neutrons in 1932. It is located in the nucleus at the center of the atom. The neutron is a charge-neutral particle and it is expressed by n.
The charge of a neutron is zero and the relative charge is also zero. The mass of the neutron is 1.674 × 10−27 kg. The number of electrons and protons in an atom is the same but the number of neutrons is different. We already know that the nucleus is at the center of the atom.
There are two types of particles in the nucleus. One is a positively charged particle proton and the other is a charge-neutral particle neutron.
Almost all the mass of the atom is accumulated in the nucleus. Therefore, the mass of the nucleus is called atomic mass. The nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons. Therefore, atomic mass refers to the total mass of protons and neutrons.
Atomic mass (A) = Nucleus mass = Total mass of protons and neutrons (p + n)
Again, the mass of each proton and neutron is about 1amu. Therefore, the total number of protons and neutrons is called the atomic mass number. That is, the number of atomic mass(A) is = p + n
Thus, the number of neutrons in an element is obtained from the difference between the number of atomic masses and the number of atoms. That is, neutron number (n) = atomic mass number (A) – atomic number (Z)
| Mass number (A) | Atomic number (Z) | Neutron number = A – Z |
| 247 | 97 | 150 |
We know that the atomic number of berkelium is 97 and the atomic average mass number is about 247. Neutron = 247 – 97 = 151. Therefore, a berkelium atom has one hundred fifty neutrons.
Based on the atomic number, mass number, and neutron number of the element, three things can be considered. These are isotope, isobar, and isotone. The number of neutrons depends on the isotope of the atom.
How to determine the number of neutrons through isotopes of berkelium?
Atoms that have the same number of protons but different mass numbers are called isotopes of each other. The English chemist Frederick Sodi first came up with the idea of isotopes in 1912, and the scientist Aston in 1919 identified two different mass neon atoms (20Ne, 22Ne).
He named the atoms with different masses of the same element as isotopes of that element. The number of protons in an isotope atom does not change but the number of neutrons does. The berkelium atom has a total of nineteen isotopes.
| Isotope | Mass number (A) | Atomic number (Z) | Neutron number = A – Z |
| 233Bk | unknown | 97 | 136 |
| 234Bk | unknown | 97 | 137 |
| 236Bk | 236.05733 | 97 | 139 |
| 238Bk | 238.05828 | 97 | 141 |
| 239Bk | 239.05828 | 97 | 142 |
| 240Bk | 239.05828 | 97 | 143 |
| 241Bk | 241.06023 | 97 | 144 |
| 242Bk | 242.06198 | 97 | 145 |
| 243Bk | 243.063008 | 97 | 146 |
| 244Bk | 244.065181 | 97 | 147 |
| 245Bk | 245.0663616 | 97 | 148 |
| 246Bk | 246.06867 | 97 | 149 |
| 247Bk | 247.070307 | 97 | 150 |
| 248Bk | 248.07309 | 97 | 151 |
| 249Bk | 249.0749867 | 97 | 152 |
| 250Bk | 250.078317 | 97 | 153 |
| 251Bk | 251.080760 | 97 | 154 |
| 252Bk | 252.08431 | 97 | 155 |
| 253Bk | 253.08688 | 97 | 156 |
Of the 19 radioisotopes of berkelium, the longest-lived radioisotope is berkelium-247 with a half-life of 1380 years. The next longest-lived berkelium isotope is berkelium-248 with a half-life of 300 years.
How many protons, neutrons and electrons does a berkelium ion(Bk3+) have?
When an atom carries a negative or positive charge by accepting or rejecting electrons, it is called an ion. The ionic properties of the elements depend on the exchange of electrons. In an atomic ion only the number of electrons changes but the number of protons and neutrons does not change.
Berkelium has only two electrons in its last orbit. During the formation of a bond, berkelium donates two electrons of the last shell and an electron in the 5f orbital to form bonds and turns into a berkelium ion(Bk3+). In this case, the berkelium ion carries a positive charge.
Bk – 3e– → Bk3+
Here, the electron configuration of berkelium ion is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 3d10 4s2 4p6 4d10 4f14 5s2 5p6 5d10 5f8 6s2 6p6.
This berkelium ion(Bk3+) has ninety-seven protons, one hundred fifty neutrons, and ninety-four electrons. The charge on the berkelium ion can change depending on the bond formation.
| Berkelium ion | Protons | Neutrons | Electrons |
| Bk3+ | 97 | 150 | 94 |
| Bk4+ | 97 | 150 | 93 |
What are the properties of protons neutrons and electrons?
| Name | Symbol | Relative Mass (amu) | Relative Charge | Actual Mass(kg) | Actual Charge(C) | Location |
| Proton | p | 1.00757 | +1 | 1.672×10−27 | 1.602×10−19 | Inside the nucleus |
| Neutron | n | 1.0089 | 0 | 1.674×10−27 | 0 | Inside the nucleus |
| Electron | e– | 5.488×10−4 | –1 | 9.109×10−31 | –1.6×10–19 | Outside the nucleus |
Why is it important for us to know the number of electrons and protons?
An atomic number is a number that carries the properties of an element. The number of electrons and protons in an element is determined by the atomic number. Also, the exact position of an element is determined in the periodic table.
The properties of an element can be determined by electron configuration. Also, the valency, valence electrons, and ionic properties of the elements are determined by the electron configuration.
To determine the properties of an element, it is necessary to arrange the electrons of that element. And to arrange the electrons, you must know the number of electrons in that element.
To know the number of electrons, you need to know the atomic number of that element. We know that an equal number of protons of atomic number are located in the nucleus of the element and electrons equal to protons are in orbit outside the nucleus.
Atomic number (Z) = Number of electrons
We already know that the atomic number of berkelium is 97. That is, there are ninety-seven electrons in the atom of the berkelium element. So, it is possible to determine the properties of berkelium from the electron configuration.
| Element Name | Berkelium |
| Symbol | Bk |
| Atomic number | 97 |
| Atomic weight (average) | 247u |
| Protons | 97 |
| Neutrons | 150 |
| Electrons | 97 |
| Group | N/A |
| Period | 7 |
| Block | f-block |
| Electrons per shell | 2, 8, 18, 32, 27, 8, 2 |
| Electron configuration | [Rn] 5f9 7s2 |
| Oxidation states | +4, +3 |
Now, the electron configuration of berkelium shows that the last shell of berkelium has two electrons and the 5f orbital has a total of nine electrons. Therefore, the valence electrons of berkelium are eleven.
The last electron of berkelium enters the f-orbital. Therefore, it’s a f-block element. To know these properties of berkelium one must know the number of electrons and protons of berkelium.
Reference